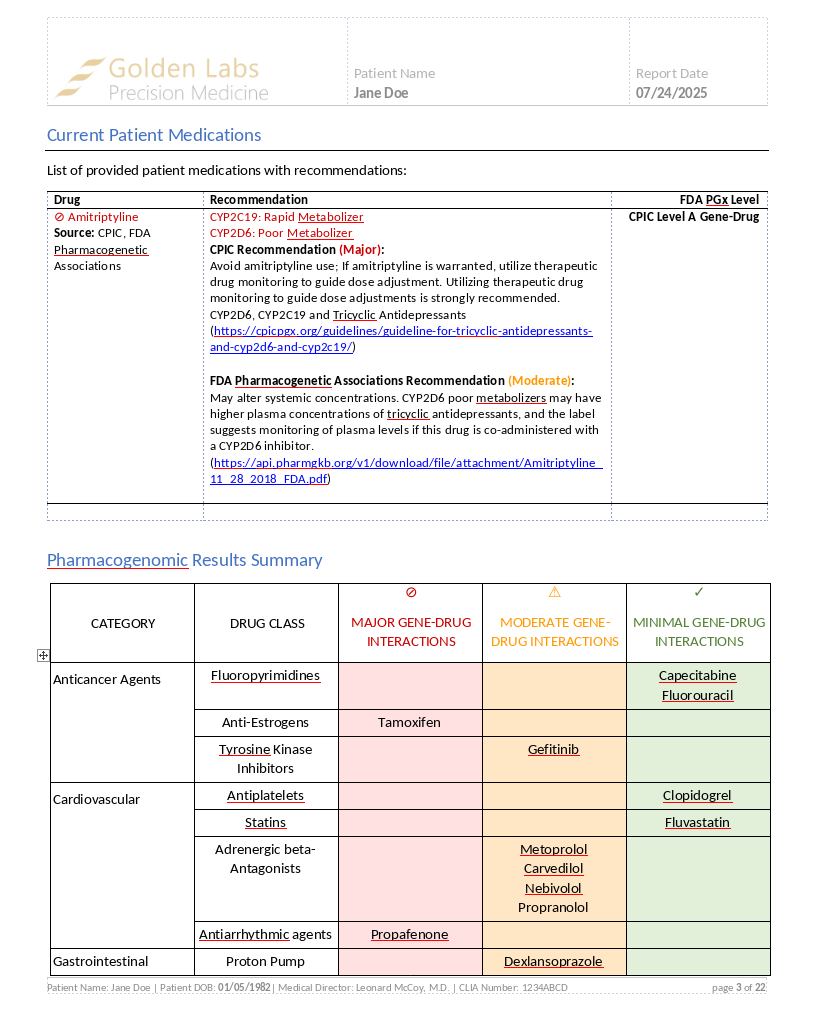
In our recent webcast, we explored how VSWarehouse 3 streamlines and automates pharmacogenomics workflows, transforming raw NGS data into actionable clinical reports. This blog post recaps the webcast, breaking down each component of the standard pharmacogenomics workflows to demonstrate how laboratories can achieve end-to-end automation in pharmacogenomic (PGx) testing.
Breaking Down the Pharmacogenomics Workflow
VSWarehouse 3 provides users with an intuitive graphical interface to visualize the various tasks involved in executing a given workflow and their dependencies. The graph below outlines the standard PGx workflow in VSWarehouse 3.
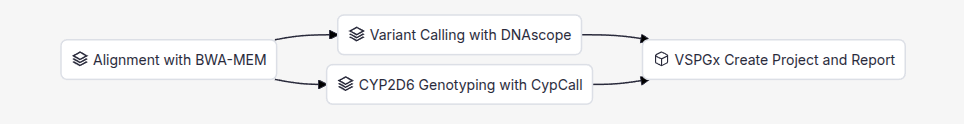
This workflow consists of four tasks, with each task automating a step of the pipeline. All tasks associated with a workflow can be customized and new tasks can be added to support the specific requirements of your institution.
Alignment with BWA-MEM
The workflow begins with the processing of raw sequencing data stored in FASTQ files. These files contain the unaligned reads generated by the sequencing platform. VSWarehouse 3 uses BWA-MEM to map these reads to the reference sequence, producing BAM alignment files which serve as the foundation for downstream analysis. Once this alignment is complete, the next two subsequent tasks are executed in parallel: variant calling and CYP2D6 genotyping.
Variant Calling with DNAScope
The first parallel task involves variant calling using Sentieon’s award-winning DNAScope algorithm. This state-of-the-art variant caller detects variants from the aligned BAMs, storing the results in VCF files. DNAScope delivers top-tier accuracy through machine learning, enhanced filtering, and improved local assembly algorithms, supporting both short and long read data from all mainstream sequencers.
CYP2D6 Genotyping with CypCall
The second parallel task addresses one of the most challenging aspects of pharmacogenomic analysis: CYP2D6 genotyping. CYP2D6 presents unique challenges due to its high sequence similarity with the CYP2D7 pseudogene. This homology results in inaccurate variant detection when using traditional variant calling methods. Additionally, accurate CYP2D6 genotyping requires specialized techniques to identify complex variations, including copy number variations (CNVs) and structural variants (SVs), which are common in this gene and can dramatically affect drug metabolism phenotypes.
To overcome these challenges, we developed CypCall. This tool was specifically designed to call CYP2D6 star allele diplotypes from whole-genome sequencing data and can detect the full spectrum of relevant genetic variation, including single-nucleotide variants (SNVs), CNVs, and SVs. Upon completion, the CypCall task uploads the inferred CYP2D6 genotypes to the Sample Catalog, where they become available for import into VarSeq.
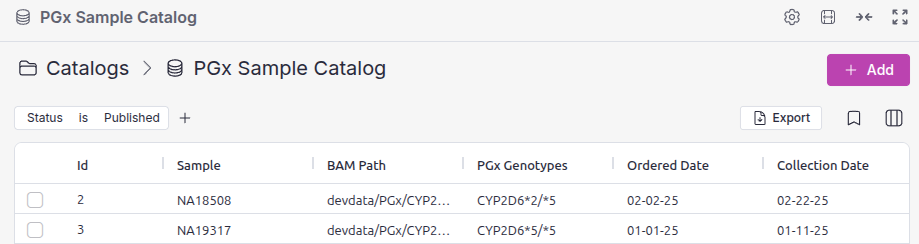
VSPGx Report Generation
Once the variant calling and CYP2D6 genotyping tasks are complete, the resulting data is imported into VarSeq, where VSPGx is used to genotype the remaining genes and generate the clinical report. The core functionality of VSPGx centers around two primary components:
- The Variant Detection and Recommendation Algorithm: This algorithm identifies pharmacogenomic diplotypes and annotates them against drug recommendations. The algorithm begins by assigning a genotype for each gene based on the variants present in the sample. For autosomal chromosomes, this process involves determining the best-matched diplotypes, which consist of paired named alleles for each pharmacogene. Once diplotypes are assigned for each gene, the algorithm maps these genetic findings to corresponding phenotypes and clinical recommendations.
- The PGx Report Generation System: Following algorithmic analysis, VSPGx leverages VarSeq’s highly customizable reporting system to generate clinical reports. The platform utilizes easy-to-modify Microsoft Word report templates, and VarSeq ships with a comprehensive PGx report template that serves as an excellent foundation for creating a custom report tailored to the specific needs of your lab.
Conclusion
VSWarehouse 3 offers a streamlined, end-to-end solution for automating complex pharmacogenomics workflows. By integrating all of the relevant bioinformatic tools into a single cohesive system, the platform enables users to move from raw sequencing data to clinically meaningful PGx reports with minimal manual intervention. If you would like to know more about VSWarehouse or our PGx capabilities, please reach out to our team at [email protected].