Automating a clinical workflow creates a stable and repeatable clinical analysis. Automation reduces the potential to introduce human error, helps in regulatory compliance, and improves the precision of the clinical results. It is important to know that if you run a sample through your clinical pipeline, you are going to get the same results today as you will in 6… Read more »
Clinical Variant Analysis – Applying ACMG Guidelines to Analyze Germline Diseases The clinical interpretation of genetic variants is time-consuming and requires strict attention to detail. Clinicians must thoroughly review any variants that could potentially cause disease using a complex set of guidelines. There are guidelines for the interpretation of variants relating to hereditary risk, germline diagnostics issued by the American… Read more »
The Beginning of Your Tertiary Analysis VarSeq is designed to be your NGS tertiary analysis solution providing users simple but in-depth means of exploring gene panel, exome, and whole genome variants. For those not accustomed to the VarSeq software, the main import file for variant analysis is the VCF. Those who are familiar with the VCF know that there can… Read more »
As our final part of the ‘Top-Quality GWAS Analysis’ blog series, we will be giving a summary of the values behind GWAS quality control and quality assessment. Performing GWAS can provide insight into the association of genetic variants with traits and complex disorders. Any novel insights into marker-phenotype associations need to be based on performing quality control steps. In this… Read more »
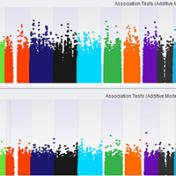
Population Stratification This article is going to cover how to factor for population stratification in your association test to continue our blog series on top quality GWAS analysis (additional articles for this series are located at the bottom of this blog). Quality control steps up to this point have included assessing sample and marker statistics, LD pruning on markers, and… Read more »
Sample Relatedness Pruning your data based on Linkage Disequilibrium (LD) values and filtering for sample “relatedness” are ideal quality assurance steps following the marker and sample quality filtering described in Part II of this blog series. The value of running an Identity by Decent estimation not only allows you to factor family relatedness in your samples but makes screening for… Read more »
Eliminate Low-Quality Samples and Markers In Part I of this GWAS Analysis series, Dr. Eli Sward provided us with a great overview on the value SVS provides in managing the quality of your SNP or NGS data to maintain the high power and accuracy of your GWAS. He also gave a snapshot of what a typical genotype spreadsheet may look… Read more »
We are happy to announce that our latest version of SVS includes the ability to call CNVs on low read depth Whole Genome Sequencing (WGS) data. Designed for calling large cytogenetic events, this algorithm can detect chromosomal aneuploidy events and other large events spanning one or more bands of a chromosome from genomes with average coverage as low as 0.05x…. Read more »
The PhoRank tool in VarSeq is further explored in this post by looking at the sample-specific capability. VarSeq PhoRank Part: 1 Variant Phorank Gene Ranking showed how the PhoRank algorithm could be applied to all the variants in a VarSeq project, regardless of the number of (or difference in) samples. There is another PhoRank algorithm in VarSeq that allows the… Read more »
One of the main goals of clinical genomic labs is to identify problematic variants in affected individuals. One tool to assist in this search is the phenotype driven variant ontological re-ranking tool in VarSeq called PhoRank. A common situation facing clinicians is sorting through thousands of variants provided by an individual’s exome data (or possibly the individual’s nuclear family exome… Read more »
In part one of this series, we discussed how the ACMG Classifier can be implemented in your filter chain to support a best practice workflow. To continue our discussion on best practices of VSClinical, this blog will shed light on other attributes of VSClinical that can add support to your evaluation. Specifically, we will explore how VSClinical can help users… Read more »
VSClinical is our most recent product that allows users to evaluate variants according to the ACMG guidelines. As with any tertiary analysis, there is a need to implement best practices into your workflow and using VSClinical for the ACMG guidelines is no exception. That said, we have put together a Best Practices Blog Series, with the purpose of discussing some… Read more »
In the first two parts of this blog, we presented examples of how to leverage Warehouse-stored VSClinical and CNV assessment catalogs in the VarSeq project. Now we are going to explore the Warehouse interface a bit more and show how to query on stored variant data. To access Warehouse from VarSeq, click the V Connect icon located in the top… Read more »
Part 1 of this blog series was focused on new capabilities in Warehouse to store your CNV results. We explored some approaches of how to utilize assessment catalogs of cohort and known pathogenic events. What makes Warehouse so useful in this application is that the catalog is accessed from one central location and ensures every user is leveraging the same… Read more »
Even though GRCh37 is currently the most widely used human genome assembly, GRCh38 provides a more complete human reference genome, offers more accurate genomic analysis, and includes centromere and mitochondrial information. However, we’re getting ahead of ourselves. Perhaps start with how we got here. The Human Genome Project started this all off with the world’s largest biological collaboration project in… Read more »
Creating Custom Scripts The first part of the Getting Started Guide for Sentieon described the steps for downloading the Sentieon tools, acquiring a license file, and running the example script/pipeline to generate the VCF and BAM files. This blog will cover some custom script changes users can make to add more efficiency when running through multiple samples at once. We… Read more »
Sentieon; your swift secondary analysis solution. Golden Helix’s software solutions present a reputable and top-quality analysis of your NGS data. Looking at this process from a 30,000 ft view, the annotation and filtering of variants in your vcf files and discovery of CNVs based coverage data in the bam file make up the tertiary level portion of the analysis. However,… Read more »
Genome-wide association studies (GWAS) are useful in genetics as they test for the association of a phenotype with common genetic variants. GWAS is “hypothesis-free” and does not require prior knowledge of a gene’s biological impact on a trait. The catch though is that this leads to analyzing hundreds to thousands of genome-wide array samples to elucidate single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) associated with a specific phenotype.
With this two-part blog series, users should now be able to perform CNV analysis using their data, set up basic quality filter standards to isolate high-quality events and utilize annotations to hone in on publicly known events as well as in-house recorded CNVs from previous projects.
2017 was a busy year regarding the development of our CNV tools. Since the release of the CNV caller, we have produced quite a bit of content tailored to assist our users with getting started. Here are some links: Robarts Research Institute CNV analysis on patients with familial hypercholesterolemia CNV annotations Common CNV questions CNV calling with shallow whole genome… Read more »