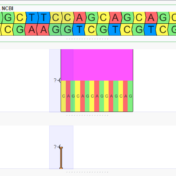
Optimizing sample throughput while maintaining quality control is, arguably, the crux of any profitable lab performing a high volume of analysis. We’ve discussed in great detail the flexibility of VSPipeline, our command line automation tool, as well as our full-stack FASTQ to report automation capabilities, and today I’d like to further elucidate on how QC methods fit into the picture…. Read more »
We’re excited to announce the release of gnomAD 4.1 variant frequencies as an annotation track in VarSeq. This latest release addresses key issues from previous versions and introduces joint variant frequencies curated directly from gnomAD. Additionally, we’ve refined our liftover process, offering more accurate GRCh37 tracks. By incorporating this data into the VarSeq data source library, we provide users with… Read more »
Reporting on Cancer Biomarkers may seem like a daunting task, both in determining the scope of what a biomarker can encompass and which information to include. Biomarkers can come in the form of small variants (SNPs and INDELs), copy number variants, and structural variants. Biomarkers can also be sourced from external cancer kits in the form of a Genomic Signature,… Read more »
Compound heterozygosity describes the relationship between two alternate alleles when they are located within the same gene but at different loci within that gene. Compound heterozygosity is particularly relevant in a recessive disorder when the presence of these alleles in combination confers an increased risk of disease, similar to a traditional homozygous recessive combination of alleles. The detection of compound… Read more »
Periodically, our FAS team will see a situation where a customer has installed VarSeq on a new machine…but something is not entirely right. Perhaps a VCF will not load, annotations cannot download, or a long-running process like coverage regions will not complete. Any of these issues alone can be tricky to troubleshoot, whether due to a permissions block, a lack… Read more »
Our customers often ask if they can include quality control metrics in their final reports. While which metrics you actually need to report may be unique to your lab, there are a variety of metrics that we can immediately render into a report, and even more that can be rendered with a few customizations. Reporting Average Coverage QC Metrics One… Read more »
There are many ways to optimize an individual workflow, from increasing the granularity of a filter chain to automating certain multi-stepped tasks. Although the best way to optimize an individual workflow is to book a session with our FAS team to talk about your unique use case, we wanted to highlight five ways a workflow can be optimized across most… Read more »
We at Golden Helix are thrilled with our recent release of gnomAD v4! The curation of this massive database was a huge undertaking for our development team, but with the addition of new features, we believe it was well worth the wait. This annotation track contains allele frequencies from a more diverse population than ever before, with the addition of… Read more »
The Broad Institute’s release of gnomAD v4 needs no introduction as the data in this release is highly sought after by professionals in the genetics community, and the v4 release has a lot to boast about! The v4 release is roughly five times larger than the v2 and v3 releases combined and includes data from 807,162 total individuals. Naturally, exome… Read more »
Today, we will be exploring the indispensable role of GenomeBrowse in your VarSeq workflows. This blog aims to guide you through various customization options, including color preferences, filtering techniques, display modifications, numeric value plotting, and additional tips. I hope to enhance your GenomeBrowse experience and enable you to gain valuable insights into your data. Let’s jump in by talking about… Read more »
The table is set, the football game is on in the background, and the family has gathered around the table when out of nowhere, your Cousin Eddie shows up for Thanksgiving dinner. While Cousin Eddie is known for eating anything, his allergies always get the best of him, ruining the evening. Thankfully, this year Cousin Eddie had recently gotten his… Read more »
Last month, the researchers at Google DeepMind announced the release of AlphaMissense, a new missense prediction algorithm that leverages the protein structure prediction model AlphaFold to distinguish between benign and pathogenic missense variants (Cheng et al., 2023). AlphaFold is a model for the prediction of protein structures from amino acid sequences. During the development of AlphaMissense, the AlphaFold model was… Read more »
Detecting CNVs from whole genome data has a number of advantages but also unique challenges. Whole genomes offer a comprehensive and uniform picture of the entire genome, allowing a user to capture CNVs at a higher resolution than with data sequenced at a lesser scale. It also allows for the detection of structural variation over non-coding regions and for a… Read more »
Assessment catalogs are a way for VarSeq users to save variants and variant information for clinically relevant variants, so when you come across this variant again in another sample, all of the work to analyze and classify the variant is already done! But there is more than meets to the eye when it comes to using assessments in VarSeq. Being… Read more »
The AMP guidelines workflow in VSClinical provides a user-friendly tool for the interpretation of somatic biomarkers across the entire spectrum of genomic variation. One of the most useful features of this workflow is its ability to streamline the evaluation of clinical evidence for a somatic biomarker using the AMP Tier evidence levels. The AMP Guidelines classify a biomarker into one… Read more »
Explore the evolving landscape of genomic analysis, transitioning from targeted gene panels to whole genome sequencing. A recent trend with our customers has been to expand their workflows from small panel sequencing analyses to larger whole exome and genome sequencing analyses. The decreasing cost of sequencing has made this a rather common request. Although more data allows for a greater… Read more »
Genomic data visualization is an extremely powerful means to help users comprehend massive amounts of sequencing data and is valuable for communicating genomic information and findings. Genome browser tools allow users to visualize aligned sequence data in BAM format, map the data to a reference assembly, view annotation tracks, genomic region tracks, export graphics for sharing, and much more. Genome… Read more »
Merging variant records, VCFs, across samples is important when performing trio or family analysis as it ensures that hereditary relationships can be properly inferred. There are many ways to represent a single variant. Insertions and deletions may be right or left aligned, prefixes and suffixes can be added, and adjacent variants in the same sample may be combined or split… Read more »
One of the many tricks of encoding so much functionality into so little space in eukaryotic genomes is the ability to produce multiple distinct mRNAs (transcripts) from a single gene. While one transcript is often the dominant one for a given tissue or cell type, there are, of course, exceptions in the messy reality of biology. It doesn’t take many… Read more »
Thank you to those who attended our recent webcast, “PhoRank 2.0: Improved Phenotype-Based Gene Ranking in VarSeq”. For those who could not attend, you can find a link to the recording here. This webcast covered upcoming improvements to the PhoRank phenotype-based gene ranking algorithm based on literature published in the years since the algorithm’s development. The PhoRank Algorithm When performing… Read more »